Tired of dreaming about your own online store but feeling paralyzed by the overwhelming choices? The digital marketplace beckons, yet the first step – deciding how to sell – can feel like navigating a minefield. Should you dive into the world of drop shipping, with its promise of low upfront costs, or forge your own path with private label, building a unique brand from the ground up? The question of Dropshipping or Private Label is very relevant now more than ever.
Imagine sinking time and resources into a model that doesn’t align with your goals. Picture the frustration of low profit margins and lack of control in dropshipping, or the daunting prospect of significant upfront investment and unsold inventory with private label.
The wrong choice can lead to wasted capital, lost time, and a deflated entrepreneurial spirit. You’re not alone in this struggle – countless aspiring e-commerce owners face this exact dilemma, unsure which path will truly unlock their potential
But what if you had a clear, unbiased guide to navigate this critical decision? This comprehensive article cuts through the noise, providing an in-depth comparison of dropshipping and private label. We’ll explore the mechanics, weigh the pros and cons, and analyze real-world examples to empower you to make an informed choice tailored to your unique circumstances.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have the clarity and confidence to choose the e-commerce model that will not just get you started, but set you on the path to lasting success
Understanding Dropshipping: The Agile Entrepreneur’s Path
What Exactly is Dropshipping? Unpacking the Mechanics In Dropshipping or Private Label
Imagine you want to open a bookstore. Traditionally, you’d need to invest in renting a space, stocking shelves with books, and managing inventory. Dropshipping flips this model on its head. Instead of holding any books yourself, you partner with suppliers who handle the storage and shipping directly to your customers.
Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Customer Places an Order: A customer visits your online store and places an order for a product you’re listing (let’s say, a quirky cat-themed mug).
You Receive the Order and Forward it: Your store receives the order and payment from the customer. You then forward this order (along with the customer’s shipping details) to your chosen supplier.
Supplier Fulfills the Order: The supplier picks, packs, and ships the cat mug directly to your customer under your store’s name (often with blind shipping, meaning your branding is on the packaging, not the supplier’s).
You Handle Customer Service: While the supplier handles the logistics, you remain responsible for customer service inquiries, returns, and building your brand’s relationship with the buyer.
Example:
Consider Sarah, who wanted to start an online store selling unique yoga mats. Instead of investing heavily in inventory, she partnered with several dropshipping suppliers who offered a variety of eco-friendly and artist-designed mats. When a customer orders a specific mat from Sarah’s website, she simply forwards the order to the corresponding supplier, who ships it directly to the customer. Sarah focuses on marketing her brand, creating engaging content, and providing excellent customer support.
The Allure of Dropshipping: Weighing the Pros In Dropshipping or Private Label
Dropshipping’s popularity stems from several compelling advantages, particularly for those just starting in e-commerce:
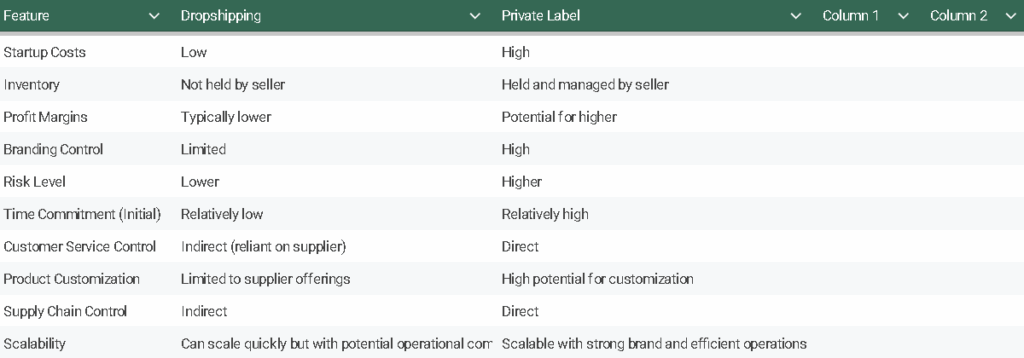
Lower Startup Costs Of Dropshipping In Choosing Btw Dropshipping or Private Label:
This is a significant draw. You don’t need to shell out large sums of money to purchase and store inventory. Your primary costs are typically setting up your online store (platform fees, website design) and marketing.
Unique Insight Online: On a Reddit thread in r/ecommercebeginners, a user asked, “What’s the cheapest way to start selling online?”. The overwhelming response highlighted dropshipping as a viable option due to the minimal upfront investment in stock.
Reduced Inventory Risk: Since you’re not holding inventory, you don’t have to worry about unsold products taking up space or becoming obsolete, leading to financial losses. This agility allows you to test different product niches without significant risk.
Example: Mark started a general store using dropshipping. He initially listed several types of phone accessories. After a few months, he noticed that uniquely designed phone cases were the best sellers. Because he wasn’t stuck with a large inventory of slow-moving items, he could easily pivot and focus on the popular designs.
Greater Product Variety: Dropshipping allows you to offer a vast selection of products without the logistical nightmare of managing them. You can easily add or remove products from your online store based on market trends and customer demand.
Specific Detail: Imagine an online store selling kitchen gadgets. Through dropshipping, they can offer everything from basic utensils to specialized appliances sourced from various suppliers, providing a comprehensive selection to their customers.
Location Flexibility: As long as you have an internet connection, you can run your dropshipping business from anywhere in the world.
1 This makes it an attractive option for digital nomads and those seeking location independence.
2. Personal Experience (Relatable Scenario): I once followed the journey of a blogger who successfully managed her dropshipping store while traveling through Southeast Asia. Her laptop was her office, and her suppliers handled the physical product aspects.
Okay, let’s delve into the other side of the coin and explore the challenges associated with dropshipping.
The Flip Side: Navigating the Challenges of Dropshipping
While dropshipping offers numerous advantages, it’s crucial to be aware of its potential pitfalls:
Lower Profit Margins: Due to the ease of entry and competitive landscape, profit margins in dropshipping can often be thinner compared to private label. You’re essentially acting as a reseller, and suppliers will typically take a larger cut. To remain competitive, you might need to keep your prices relatively low, impacting your profitability per sale.
Actionable Step: To mitigate this, focus on finding niche products with less competition, building a strong brand that allows for slightly higher pricing, and optimizing your marketing efforts to increase sales volume.
Reliance on Suppliers:
This is a significant drawback. You are entrusting crucial aspects of your business – product quality, shipping speed, and inventory management – to third-party suppliers. If a supplier makes a mistake (sends the wrong item, ships late, or has quality control issues), it reflects poorly on your business and can damage your reputation.
Unique Insight Online: I’ve seen numerous complaints on r/dropship about unreliable suppliers. One user recounted a situation where their supplier consistently shipped damaged goods, leading to a flood of customer complaints and chargebacks, ultimately harming their store’s reputation.
Inventory Management Complexities (Indirect): Although you don’t hold the inventory yourself, keeping track of stock levels across multiple suppliers can be challenging. A product listed as available on your store might be out of stock with the supplier, leading to order cancellations and customer dissatisfaction.
Specific Context: Utilizing inventory management software that integrates with your suppliers’ systems can help mitigate this risk by providing real-time stock updates. However, these systems aren’t always foolproof, and manual checks are often still necessary.
Branding Limitations: Building a strong, recognizable brand can be difficult with dropshipping. You have limited control over the product itself, its packaging, and the overall customer experience beyond your own website and customer service interactions. The products often feel generic, making it harder to create a unique identity in the market.
Example: Imagine two online stores selling similar Bluetooth speakers via dropshipping. One store simply lists the product with a generic description, while the other invests in creating high-quality product photos, writing compelling descriptions that highlight a specific lifestyle, and offers excellent post-purchase support. The latter has a better chance of building a loyal customer base, even though they don’t control the manufacturing.
Defining Private Label: Crafting Your Own Identity
Private label takes a fundamentally different approach to e-commerce. Instead of reselling existing products, you work with a manufacturer or supplier to produce goods specifically under your own brand name and packaging. Think of it like a supermarket that sells its own “store brand” of pasta or coffee – the product is manufactured by someone else but sold exclusively under the supermarket’s label.
Here’s a breakdown of the private label process:
Your Brand Vision: You start with an idea for a product or a specific niche you want to cater to. This involves market research to identify opportunities and define your target audience.
Product Sourcing/Manufacturing: You then find a manufacturer or supplier who can produce your desired product according to your specifications. This might involve customizing existing products or creating entirely new ones.
Your Branding & Packaging: You invest in creating your own brand identity, including your logo, brand colors, and packaging design. This is crucial for differentiating your products and building brand recognition.
Selling Under Your Brand: You then sell these branded products directly to consumers through your own online store or other sales channels. You have complete control over your product listings, pricing, and marketing.
Example:
Consider a fitness enthusiast named Alex who noticed a gap in the market for high-quality, eco-friendly resistance bands with unique resistance levels. Alex researched manufacturers, developed specific material and tension requirements, designed his brand logo and packaging, and now sells these custom-made resistance bands under his brand name through his own website.
The Power of Ownership: Exploring the Advantages of Private Label In Dropshipping or Private Label
The private label model offers significant advantages for entrepreneurs looking to build a lasting brand and achieve greater control:
Higher Profit Margins: Because you are essentially creating your own product and brand, you have more control over pricing and can often achieve higher profit margins compared to dropshipping. Your perceived value is tied to your unique brand and product quality, not just the base product cost.
Actionable Step: Conduct thorough cost analysis during the sourcing phase to optimize your production costs and determine a profitable yet competitive retail price.
Stronger Brand Building: Private label provides the opportunity to create a unique brand identity, cultivate customer loyalty, and build a strong brand reputation. Your packaging, marketing materials, and customer service all contribute to your brand narrative.
Specific Detail: Think about brands like Glossier in cosmetics or Gymshark in fitness apparel. Their success is heavily reliant on their strong brand identity and the community they’ve built around it, which is only truly achievable through owning the brand.
Greater Control Over Product Quality and Supply Chain: You have the ability to choose your manufacturers, implement rigorous quality control processes, and potentially build long-term relationships with reliable suppliers. This direct control minimizes the risk of inconsistencies and ensures your products meet your brand’s standards.
Personal Experience (Relatable Scenario): I recall reading about a private label food company that personally visited their ingredient suppliers to ensure ethical sourcing and high-quality standards, a level of control simply not possible with dropshipping.
Direct Customer Relationships: With private label, you own the entire customer experience. This allows you to gather direct feedback, build relationships, and tailor your products and services to better meet your customers’ needs, fostering loyalty and repeat purchases.
Unique Insight Online: On a Quora forum discussing brand building, a private label business owner emphasized the invaluable insights gained from direct customer feedback, which directly influenced their product development and marketing strategies.
Navigating the Terrain: Addressing the Challenges of Private Label In Dropshipping or Private Label
While the rewards of private label can be significant, it’s essential to acknowledge the challenges that come with greater ownership and control:
Higher Startup Costs: Entering the private label arena typically requires a more substantial initial investment compared to dropshipping. You’ll need to factor in costs for product development (if applicable), sourcing or manufacturing setup, initial inventory purchase, branding and packaging design, and potentially warehousing.
Actionable Step: Develop a detailed financial plan that outlines all potential startup costs. Explore funding options such as small business loans, lines of credit, or bootstrapping through personal savings.
Inventory Management Responsibilities: Unlike dropshipping, you are responsible for managing your own inventory. This includes forecasting demand, storing products (which may require renting warehouse space), and dealing with potential issues like spoilage, damage, or unsold stock. Effective inventory management is crucial to avoid losses.
Specific Context: Implementing an inventory management system is vital for private label businesses. This software can help track stock levels, predict demand, and optimize your supply chain to minimize holding costs and prevent stockouts.
Increased Risk: Investing in your own inventory carries a higher financial risk. If your products don’t sell as anticipated, you could be left with a significant amount of unsold goods, leading to potential write-offs and losses. Thorough market research and validation are crucial to mitigate this risk.
Example: A new private label clothing brand overestimated the demand for a particular style of jacket. They invested heavily in manufacturing a large quantity, but sales were slow, resulting in a significant amount of unsold inventory that they eventually had to sell at a steep discount.
Longer Time to Market: Bringing a private label product to market often takes more time than starting with dropshipping. You’ll need to go through the processes of product development (if custom), sourcing and vetting manufacturers, designing packaging, and potentially navigating regulatory requirements before you can even begin selling.
Unique Insight Online: On a Reddit thread in r/smallbusiness, several private label owners discussed the surprisingly long lead times involved in finding reliable manufacturers and finalizing product designs, emphasizing the need for patience and thorough planning.
Navigating the Terrain: Addressing the Challenges of Private Label In Dropshipping or Private Label
While the rewards of private label can be significant, it’s essential to acknowledge the challenges that come with greater ownership and control:
Higher Startup Costs: Entering the private label arena typically requires a more substantial initial investment compared to dropshipping. You’ll need to factor in costs for product development (if applicable), sourcing or manufacturing setup, initial inventory purchase, branding and packaging design, and potentially warehousing.
Actionable Step: Develop a detailed financial plan that outlines all potential startup costs. Explore funding options such as small business loans, lines of credit, or bootstrapping through personal savings.
Inventory Management Responsibilities: Unlike dropshipping, you are responsible for managing your own inventory. This includes forecasting demand, storing products (which may require renting warehouse space), and dealing with potential issues like spoilage, damage, or unsold stock. Effective inventory management is crucial to avoid losses.
Specific Context: Implementing an inventory management system is vital for private label businesses. This software can help track stock levels, predict demand, and optimize your supply chain to minimize holding costs and prevent stockouts.
Increased Risk: Investing in your own inventory carries a higher financial risk. If your products don’t sell as anticipated, you could be left with a significant amount of unsold goods, leading to potential write-offs and losses. Thorough market research and validation are crucial to mitigate this risk.
Example: A new private label clothing brand overestimated the demand for a particular style of jacket. They invested heavily in manufacturing a large quantity, but sales were slow, resulting in a significant amount of unsold inventory that they eventually had to sell at a steep discount.
Longer Time to Market: Bringing a private label product to market often takes more time than starting with dropshipping. You’ll need to go through the processes of product development (if custom), sourcing and vetting manufacturers, designing packaging, and potentially navigating regulatory requirements before you can even begin selling.
Unique Insight Online: On a Reddit thread in r/smallbusiness, several private label owners discussed the surprisingly long lead times involved in finding reliable manufacturers and finalizing product designs, emphasizing the need for patience and thorough planning.
LSI Keywords: As you consider these models, remember that the broader landscape of e-commerce business models offers various online retail strategies. Understanding your product fulfillment options is key to making the right choice.
Who Wins Where? Tailoring the Choice to Your Goals In Dropshipping or Private Label
The “better” model isn’t universal; it depends entirely on your individual goals, resources, and risk tolerance. Let’s explore some scenarios:
Use Case 1: The Budget-Conscious Beginner: Imagine someone with limited capital but a strong desire to enter e-commerce. They want to test the waters and learn the fundamentals without significant financial risk.
Why Dropshipping Might Be a Better Fit: The low startup costs of dropshipping make it an accessible entry point. They can experiment with different niches and products without a large upfront investment in inventory. The focus can be on learning marketing, customer service, and the basics of running an online store.
Specific Details: They can start with a platform like Shopify or Etsy, utilizing free or low-cost themes and focusing on organic traffic or low-budget social media marketing to validate product ideas.
Use Case 2: The Brand Builder with a Vision: Consider an entrepreneur with a unique product idea or a passion for creating a specific brand identity and customer experience. They are focused on long-term growth and building a loyal customer base.
Why Private Label is More Suitable: Private label offers the control needed to bring their unique product vision to life and build a distinct brand. They can focus on quality, packaging, and creating a strong emotional connection with their target audience.
Specific Details: This individual might invest in professional branding services, custom packaging, and build their online store with a focus on brand storytelling and customer engagement.
Use Case 3: The Scalability Seeker: Think about someone who has already experienced some success in e-commerce and is looking to scale their business for sustainable growth and higher profitability.
Which Model Offers Better Long-Term Scalability: While both models can be scaled, private label often offers greater long-term scalability due to stronger brand loyalty, higher profit margins, and more control over the product and supply chain. This allows for reinvestment in marketing, product development, and building a more robust business infrastructure. Dropshipping can face scalability challenges related to maintaining quality control and consistent customer experience as order volumes increase across multiple suppliers.
Specific Details: A private label brand can expand its product line under its established brand name, build a direct-to-consumer model, and potentially explore wholesale opportunities, leading to more sustainable growth.
Real-World Success Stories: Inspiration from Both Paths In Dropshipping or Private Label

It’s inspiring to see how both models can lead to successful e-commerce ventures:
Dropshipping Success Story: Consider a store like “OddityMall” (while they might have evolved, they often started with a curated dropshipping model). They built a successful business by expertly curating unique and interesting gadgets from various suppliers, focusing on strong marketing, engaging content, and providing good customer service despite not holding the inventory themselves.
Private Label Success Story: Look at “Beardbrand.” They identified a niche market (men’s grooming), developed their own line of high-quality beard care products, invested heavily in branding and content marketing, and built a loyal community. Their success is directly tied to their unique brand and product quality.
Making the Right Choice: A Step-by-Step Guide Dropshipping or Private Label
Choosing between dropshipping and private label is a significant decision. By carefully considering the following steps, your readers can gain clarity and make a well-informed choice.
Step 1: Define Your Goals and Resources In Dropshipping or Private Label:
Before even thinking about products or suppliers, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of your own objectives and the resources you have available. Ask yourself:
What is your budget for starting? Be realistic about the capital you can invest upfront. Dropshipping generally requires less initial capital than private label.
How much time can you realistically dedicate? Both models require effort, but private label often demands more time initially for product development and branding. Consider your current commitments and how much time you can allocate to your e-commerce venture.
What is your risk tolerance? Are you comfortable with the higher financial risk associated with holding your own inventory, or do you prefer the lower risk of dropshipping?
Do you have a specific product idea or niche in mind? If you have a unique product vision, private label might be the more direct route. If you’re still exploring, dropshipping can be a good way to test different niches.
What are your long-term aspirations for the business (brand building, scalability)? If building a strong, recognizable brand is a top priority, private label offers more control. If rapid scaling with less initial overhead is the focus, dropshipping might be appealing initially.
Step 2: Research Your Niche and Target Audience In Dropshipping or Private Label:
Regardless of the model you choose, thorough market research is paramount. Understand:
Demand: Is there sufficient demand for the products you’re considering selling? Use tools like Google Trends, keyword research tools, and competitor analysis to gauge interest.
Actionable Step: Explore subreddits related to your niche (e.g., r/skincareaddiction for skincare products) to understand customer pain points, desires, and frequently asked questions. Analyze popular threads and identify unmet needs.
Competition: Analyze your potential competitors. What are their strengths and weaknesses? How can you differentiate yourself?
Actionable Step: Look at product reviews on competitor websites and platforms like Amazon. Identify common complaints or areas where customers feel underserved. This can reveal opportunities for your own product or service.
Profitability: Can you realistically achieve profitable margins in your chosen niche with either dropshipping or private label, considering costs like marketing, supplier fees (for dropshipping), or manufacturing costs (for private label)?
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers/Manufacturers In Dropshipping or Private Label:
The quality and reliability of your partners are critical for both models:
Dropshipping: Research potential suppliers on platforms like AliExpress, SaleHoo, or Spocket. Look for reliable suppliers with good reviews, fast shipping times, and quality products.
Actionable Step: Order samples from potential dropshipping suppliers to assess product quality and shipping times firsthand. Communicate with them to gauge their responsiveness and professionalism.
Private Label: Identify potential manufacturers or sourcing agents through platforms like Alibaba, ThomasNet, or industry-specific trade shows. Focus on those who can meet your quality standards and production requirements.
Actionable Step: Request quotes from multiple manufacturers, inquire about their quality control processes, minimum order quantities (MOQs), and production timelines. If possible, visit their facilities or request detailed product samples.
Step 4: Consider Your Branding Strategy (Even for Dropshipping)In Dropshipping or Private Label:
While branding is more central to private label, it’s still important for dropshipping:
Dropshipping: Focus on building a strong brand identity through your store name, logo, website design, customer service, and marketing efforts. Even though you don’t control the product, you control the customer experience.
Private Label: Develop a comprehensive branding strategy that includes your brand name, logo, visual identity, brand voice, packaging design, and overall customer experience. This is a key differentiator and a long-term asset.
Step 5: Plan Your Marketing and Sales Channels In Dropshipping or Private Label:
How will you reach your target audience and drive sales?
Both Models: Consider various marketing channels such as social media marketing, SEO (Search Engine Optimization), paid advertising (e.g., Google Ads, Facebook Ads), email marketing, and content marketing.
Specific Context: Research which platforms and strategies are most effective for your target audience and the type of products you plan to sell. For visually appealing products, platforms like Instagram and Pinterest might be key. For information-driven products, content marketing and SEO could be more effective.
Step 6: Understand the Legal and Operational Aspects In Dropshipping or Private Label:
Don’t overlook the essential behind-the-scenes elements:
Business Registration: Understand the legal requirements for starting an online business in your location (remembering you are in Kenya).
Payment Processing: Set up secure and reliable payment gateways.
Customer Service Policies: Establish clear policies for returns, refunds, and customer inquiries.
Shipping and Fulfillment (for Private Label): Plan your shipping strategy and potentially set up warehousing and fulfillment processes.
By working through these steps thoughtfully, your readers will be much better equipped to determine whether dropshipping or private label is the right path to unlock their e-commerce potential.
Alright, let’s venture beyond the fundamental aspects of dropshipping and private label and explore more advanced strategies and emerging trends in the e-commerce landscape.
VI. Beyond the Basics: Advanced Strategies and Future Trends In Dropshipping or Private Label
Once you have a foundational understanding of dropshipping and private label, you can start exploring more sophisticated approaches to optimize your business and stay ahead of the curve.
Hybrid Models: Blending Dropshipping and Private Label In Dropshipping or Private Label:
The choice between dropshipping and private label isn’t always binary. Many successful e-commerce businesses adopt hybrid models that leverage the strengths of both approaches:
Starting with Dropshipping, Transitioning to Private Label: This is a common and often strategic path. You can begin by dropshipping various products within your niche to identify best-sellers and validate market demand without significant upfront investment. Once you have data on consistently popular items, you can then invest in private labeling those specific products to gain better control over quality, branding, and profit margins.
Example: An online store selling eco-friendly home goods might initially dropship a range of sustainable products. After noticing consistent high sales for bamboo cutlery sets, they could then work with a manufacturer to create their own branded bamboo cutlery with unique designs and packaging.
Combining Dropshipped and Private Label Products: You might offer a core range of your own private label products while supplementing your catalog with dropshipped items to offer greater variety without the inventory burden for less popular or niche products.
Example: A private label fitness apparel brand might offer its own branded leggings and sports bras while dropshipping accessories like yoga mats or resistance bands from other suppliers.
H2: The Role of Technology and Automation:
Leveraging technology and automation tools can significantly streamline operations for both dropshipping and private label businesses:
E-commerce Platforms: Platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, and BigCommerce offer robust features for managing your online store, processing orders, and integrating with various apps.
Automation Software: Tools for email marketing automation (e.g., Mailchimp, Klaviyo), social media scheduling (e.g., Hootsuite, Buffer), and customer service (e.g., Zendesk, Intercom) can save time and improve efficiency.
Inventory Management Software (Crucial for Private Label): As mentioned earlier, systems like Zoho Inventory, Cin7, or Katana MRP are essential for tracking stock levels, managing purchase orders, and forecasting demand for private label businesses.
Dropshipping Automation Tools: Apps like Oberlo (for Shopify) or DSers (for AliExpress) can automate the process of importing products, fulfilling orders, and tracking shipments for dropshipping businesses.
AI-Powered Tools: Increasingly, AI is being used for tasks like product recommendation engines, personalized marketing, and even generating product descriptions.
Emerging Trends in E-commerce In Dropshipping or Private Label:
Staying informed about emerging trends can provide a competitive edge:
Sustainable E-commerce: Consumers are increasingly conscious of environmental and social responsibility. Offering eco-friendly products, sustainable packaging, and transparent sourcing practices can resonate with this growing market.
Personalization: Tailoring product recommendations, marketing messages, and the overall shopping experience to individual customer preferences can enhance engagement and drive sales.
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Brands: More brands are bypassing traditional retail channels and selling directly to consumers online, allowing for greater control over branding and customer relationships (this is inherently aligned with the private label model).
The Rise of Social Commerce: Selling directly through social media platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook is becoming increasingly popular.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): While still in their early stages for many small businesses, AR and VR offer immersive shopping experiences, allowing customers to visualize products in their own space before purchasing.
Faster and More Flexible Shipping Options: Consumers expect quick and convenient delivery. Offering various shipping options and potentially partnering with local couriers in Kenya can improve customer satisfaction.
Expert Insights: Perspectives from Industry Leaders (Optional) In Dropshipping or Private Label:
Incorporating quotes or brief insights from e-commerce experts or successful entrepreneurs in Kenya could add credibility and unique perspectives to your article. You could reach out to local e-commerce communities or interview individuals who have successfully navigated the dropshipping or private label landscape in the Kenyan market.
By considering these advanced strategies and staying abreast of emerging trends, your readers can move beyond the basics and build more resilient and successful e-commerce businesses, regardless of whether they choose the dropshipping or private label path.
Conclusion: Empowering Your E-commerce Journey
Dropshipping presents a compelling entry point, particularly for aspiring entrepreneurs in Kenya with limited capital. Its lower startup costs and reduced inventory risk allow for experimentation and learning the ropes of online sales without significant financial exposure.
However, it’s crucial to be mindful of the potential for lower profit margins and the reliance on supplier quality and efficiency – factors that require careful vetting of partners within the Kenyan or international supply chain.
On the other hand, private label offers the exciting opportunity to build a unique brand, establish stronger customer relationships, and potentially achieve higher profit margins. For Kenyan entrepreneurs with a distinct product vision and a desire for greater control, private label can pave the way for a sustainable and impactful business.
However, it demands a more significant upfront investment and a thorough understanding of inventory management and the local regulatory landscape for manufacturing and importation, if applicable.
Ultimately, there is no universally “better” model. The optimal choice hinges on your individual circumstances, your vision for your business, and the resources you have at your disposal. Consider the steps outlined in this guide – from defining your goals to researching your niche and evaluating potential partners, keeping the unique dynamics of the Kenyan market in mind.
Whether you choose the agile path of dropshipping or the brand-building journey of private label, remember that success in e-commerce requires dedication, continuous learning, and a customer-centric approach. Embrace the opportunities 1 that the digital marketplace in Kenya and beyond offers, and don’t be afraid to adapt and evolve your strategy as you grow.
Take some time to reflect on the insights shared in this article and honestly assess your goals and resources. Which model resonates most with your aspirations? What are the first three actionable steps you can take today to move closer to launching your e-commerce venture?
The potential to unlock your e-commerce success is within reach. Choose your path wisely, embrace the journey, and never stop learning when choosing between Dropshipping or Private Label to get whats right for you. Follow marginseyedigital.com for more.
